Get Started with Our Kannada Typing Tool
Our Kannada typing tool makes it easy to type in Kannada without any technical knowledge or software downloads. All you need to do is visit our website and start typing! Our intuitive layout ensures that you`ll be able to quickly navigate the page and get started with your typing. Best of all, you don`t have to worry about accuracy - our tool will automatically detect and correct mistakes as you type! In mobile when you type in all the given text-area space, your content fills the text-area and if you want to increase the size of the text area, you can expand its size each time you press the button EXPAND and after completion and start a new content typing press the button SHRINK and the text area will be back to its original size. On the desktop, once the text has been typed into the desired language, all you need to do is select it all, press “ctrl-c,” copy it, and then press “ctrl-v” to paste it back into your document. When you are on mobile just simply click the COPY button and copy all your text and then paste it into your desired location. And also clear your text area after typing press the CLEAR button and you can type other contents as you like.
Unable to find the correct transliterate?
Kannada Language
Kannada is a Dravidian language spoken primarily in the Indian state of Karnataka, as well as in the neighboring states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Kerala, and Goa. Kannada is written in the Kannada script, which is a member of the Brahmic family of scripts.
History of Kannada
Kannada has a rich and ancient history. The earliest known inscriptions in the Kannada language date back to the 6th century AD, and they provide evidence of the development of the Kannada script, literature, and culture in the region. The earliest known Kannada literature is the "Kavirajamarga", a treatise on poetry and grammar written in the 9th century AD by the poet and scholar Nripatunga.
During the 12th and 13th centuries AD, Kannada literature reached its peak with the works of the poet Janna and the philosopher-statesman Basavanna, who contributed to the development of Vachana poetry and the Lingayat religious movement.
In the following centuries, Kannada literature continued to flourish, with notable contributions from poets and writers such as Raghavanka, Harihara, and Kumara Vyasa. During the British colonial period, Kannada literature and culture faced suppression, but it continued to evolve and adapt to changing times, resulting in a rich and diverse tradition.
In the modern era, the Kannada language and literature have been revitalized through the efforts of scholars, writers, and activists, and it continues to play an important role in the cultural and intellectual life of the state of Karnataka and the Kannada-speaking community.
Kannada Script (ಕನ್ನಡ ಲಿಪಿ)
Consonants (ವ್ಯಂಜನಗಳು)
k (ಕ), kh (ಖ), g (ಗ), gh (ಘ), ṅ (ಙ), c (ಚ), ch (ಛ), j (ಜ), jh (ಝ), ñ (ಞ), ṭ (ಟ), ṭh (ಠ), ḍ (ಡ), ḍh (ಢ), ṇ (ಣ), t (ತ), th (ಥ), d (ದ), dh (ಧ), n (ನ), p (ಪ), ph (ಫ), b (ಬ), bh (ಭ), m (ಮ), y (ಯ), r (ರ), l (ಲ), v (ವ), ś (ಶ), ṣ (ಷ), s (ಸ), h (ಹ)
Additional Consonants (ಹೆಚ್ಚುವರಿ ವ್ಯಂಜನಗಳು)
jñ (ಝ್ಞ), tr (ತ್ರ), tṟ (ತೃ), dr (ದ್ರ), dṟ (ದೃ), nṭ (ನ್ತ), nḍ (ನ್ದ), nṇ (ನ್ನ), ṉ (ನ್)
Vowels (ಸ್ವರಗಳು)
a (ಅ), ā (ಆ), i (ಇ), ī (ಈ), u (ಉ), ū (ಊ), e (ಎ), ē (ಏ), ai (ಐ), o (ಒ), ō (ಓ), au (ಔ)
Additional Vowels (ಹೆಚ್ಚುವರಿ ಸ್ವರಗಳು)
e (ಎ), ē (ಏ), ai (ಐ), o (ಒ), ō (ಓ), au (ಔ)
Numbers (ಸಂಖ್ಯೆಗಳು)
1 - ೧ (oṇṭu), 2 - ೨ (yēru), 3 - ೩ (mūru), 4 - ೪ (nālku), 5 - ೫ (āydu), 6 - ೬ (yēṇṭu), 7 - ೭ (yēḷu), 8 - ೮ (yēṭṭu), 9 - ೯ (yēṅṅu), 10 - ೧೦ (hattu)
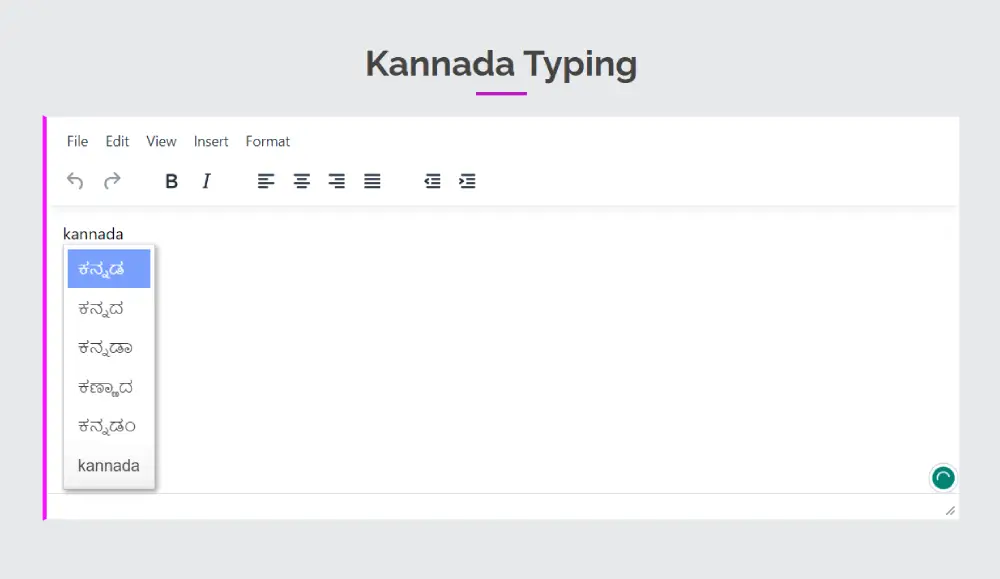
Transliterate English to Kannada
Our online typing system will allow you to transliterate English into Kannada. We use the Google transliterate feature to translate, which is very fast and accurate. You can simply convert each word, just press the space bar after typing them. Also, you can get a choice option dropdown if you press the back key. You can edit your text with a text editor to bold, italic etc. Format and style all your converted Kannada content. We use some autocorrection features to transliterate your broken words without retyping them. Which saves you more time in typing.
Press (Ctrl+G) to switch between English and Kannada. Also, you can save them as txt or doc for your further use.
Translate vs Transliterate
Translation refers to the process of converting written text from one language to another while preserving the meaning of the original text. Translation involves converting the words and phrases of a text from one language to their equivalents in another language, taking into account the context and cultural differences between the languages.
Transliteration, on the other hand, refers to the process of converting written text from one script (alphabet or writing system) to another, while preserving the sounds of the original text. Transliteration involves converting the letters and characters of a text from one script to their equivalents in another script, without necessarily preserving the meanings of the words.
For instance, the Kannada equivalent of the English phrase "Hello, how are you?" is "ಹಲೋ, ಹೇಗಿದ್ದೀಯಾ?" This translation keeps the original phrase`s meaning. On the other hand, the English phrase "Hello, how are you?" can be transliterated into the Kannada alphabet as "ಹಲೋ, ಹೌ ಅರೆ ಯು?", which preserves the sounds of the original phrase but not necessarily it`s meaning.
Translation and transliteration are both useful tools for helping people communicate and understand written text in different languages and scripts. However, they serve different purposes and involve different approaches to converting written text.
